Entando 6.3
The leading micro frontend platform for Kubernetes just got better. Entando 6.3 brings exciting updates for DevOps and developers that enable you to innovate more quickly.
What's New
The 6.3 release of the Entando platform brings significant new features, bug fixes and architectural updates to speed the development of your micro frontend applications on Kubernetes. The goal of the release is to enhance the platform in three key areas.
Streamlined Developer and User Experience
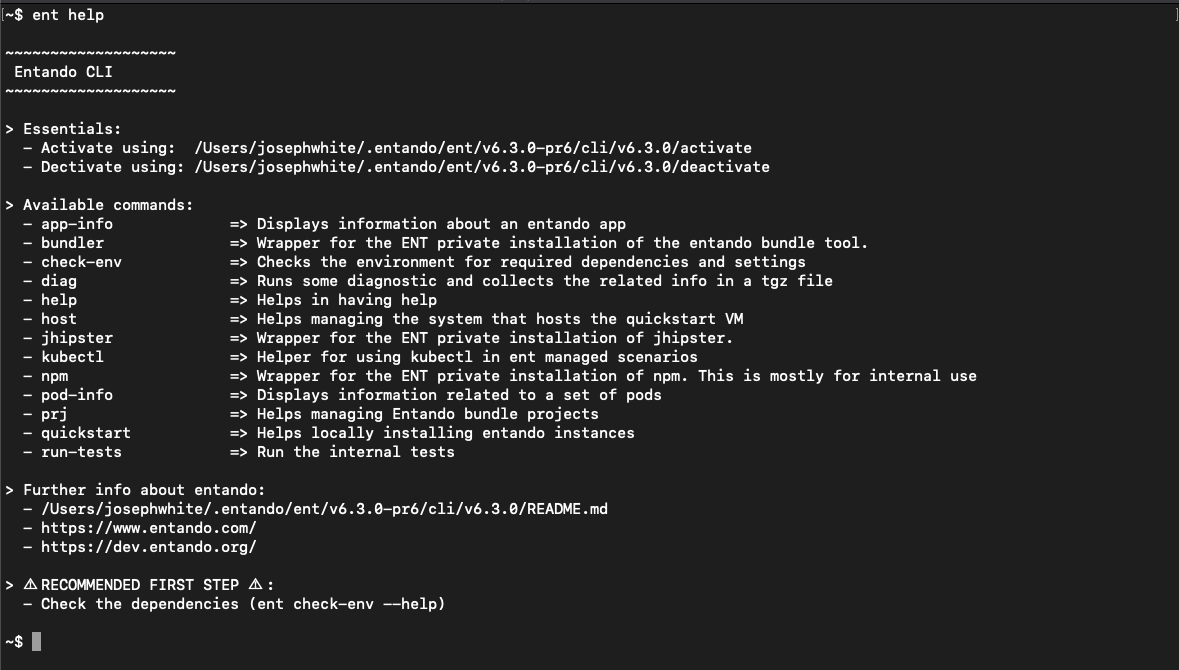
ENTANDO COMMAND LINE INTERFACE (CLI)
The "ent" CLI is a powerful new CLI with 1-line commands to quickly generate, manage, and deploy projects including micro frontends, microservices, pages, and content.
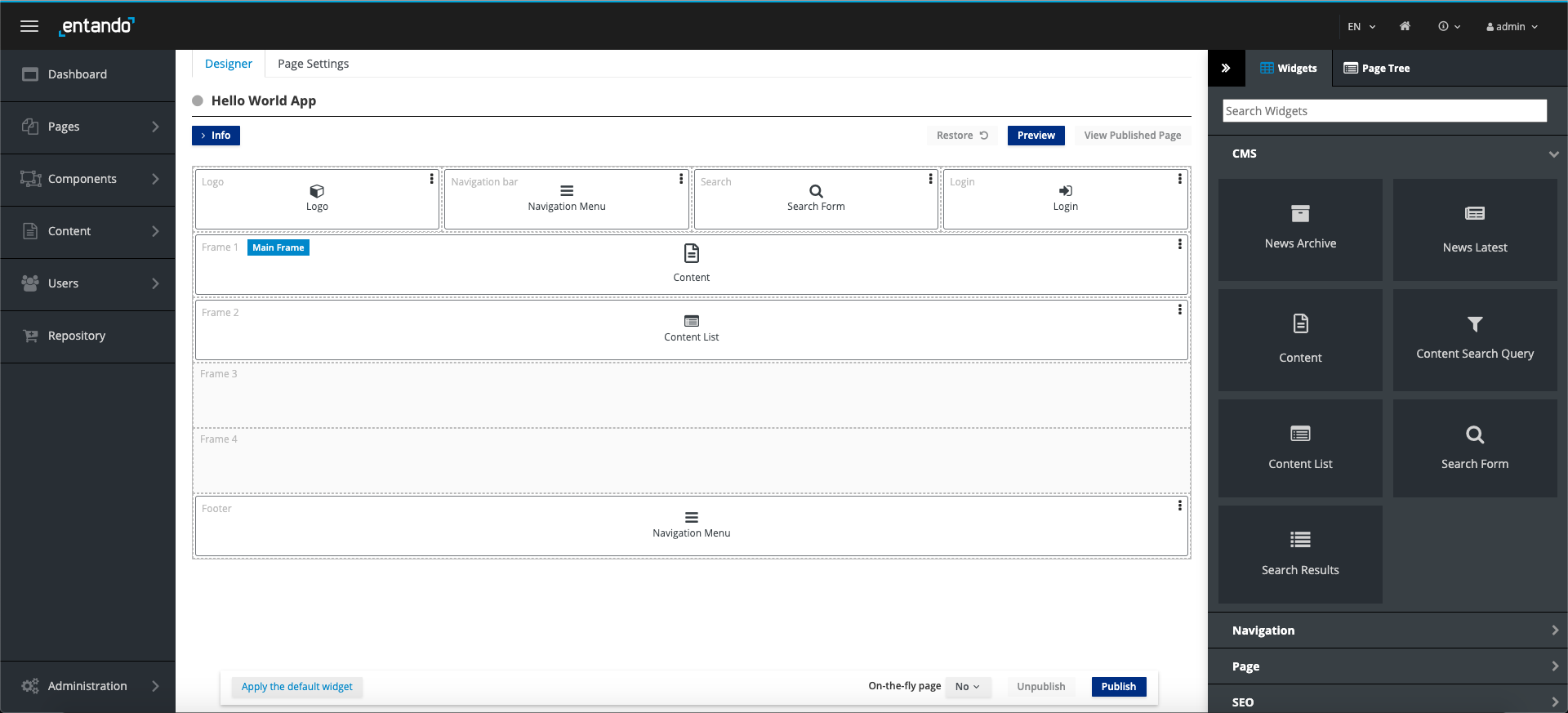
NEW OUT-OF-THE-BOX PAGE TEMPLATES, CONTENT TEMPLATES, AND WIDGETS
With the release of 6.3 Entando ships with a set of templates to help accelerate the application development process and to provide a set of examples to work from for developers new to Entando.
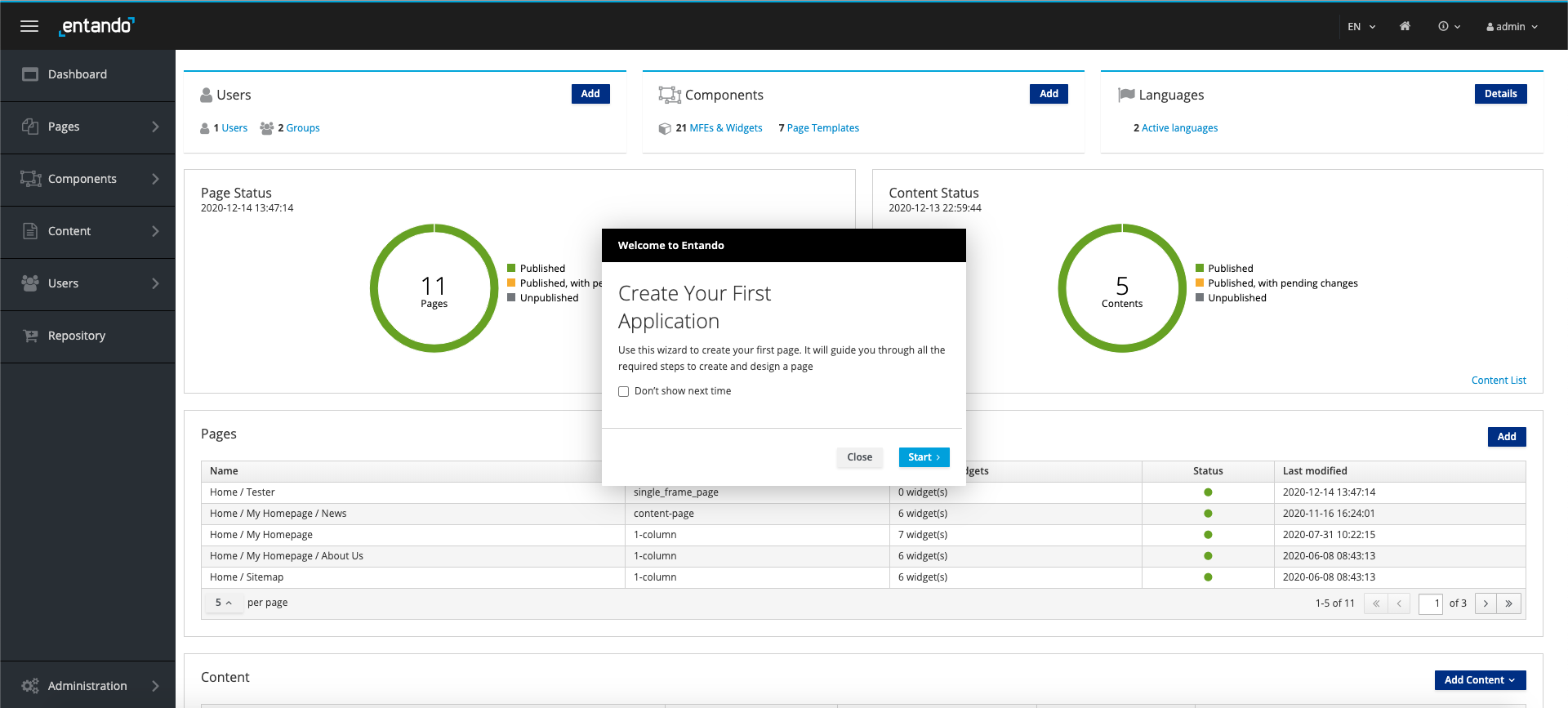
WELCOME WIZARD
The Entando App Builder now includes an interactive tutorial to give new developers and users an introduction to creating Entando applications.
SINGLE DOMAIN DEPLOYMENT OPTIONS
When deploying to a Kubernetes cluster the Entando platform now supports configuration under a single domain. In particular, this update will greatly simplify the deployment of the platform on Windows and in cases where local network settings prevent the resolution of DNS services like nip.io or xip.io.
Bundling, Distribution, and Reuse
AUTOMATED BUNDLE CREATION
In concert with the ent CLI tool the Entando 6.3 release includes new capabilities to create bundles from running Entando applications. The bundle tool is built to aid in developer workflows to support fast reuse and customization across Entando applications.
NEW COMPONENTS
The 6.3 release includes a significant expansion of the types of components that can be included in an Entando bundle and deployed via the Entando Component Repository.
ECR UPDATE STRATEGIES
The Entando Component Repository provides new features for component lifecycle management that allows developers to force the installation of a component in a given Entando application.
Kubernetes Deployment Architecture and Operational Automation
PRIVATE REPOSITORIES AND AIR GAPPED INSTALLATION
This release includes significant simplification in using private Docker registries for custom image deployment and private GitHub repositories for hosting Entando bundles. In both cases the Entando operator supports the management of Kubernetes secrets to ensure that credentials are stored and accessed securely.
CENTRALIZED OPERATOR
The centralization of the Entando Operator allows operations teams to isolate the operator functionality to manage the lifecycle and operations of many Entando applications in a cluster.
NEW CLUSTERING OPTIONS FOR ENTANDO APP ENGINE
The Entando App Engine supports new high availability and horizontal scaling options with the 6.3 release. The updates are focused on updates to the caching layer including a new implementation using Redis or via Infinispan with JGroups and KUBE_PING.
PROXIES AND TLS TERMINATION
In many enterprise deployments , customers have an external proxy that will utilize HTTPS that operates independently of K8S and will supersede the TLS functionality provided by K8S ingresses. With this release Entando supports more complex TLS and network topologies including allowing components internal to a cluster to communicate via HTTPS.
Libraries and Key Version Updates
JAVA 11 REQUIRED
With the release of 6.3, Entando now requires Java 11 for all of the Entando base images for enhanced encryption and security. All of the images deployed as part of the 6.3 release have been updated to use OpenJDK Java 11.
DEPENDENCY AND LIBRARY UPDATES
The 6.3 release also includes significant changes and updates to the libraries used by the different services in the Entando architecture. As part of our deployment and pipeline process we include vulnerability scanning via Sonar and OWASP detection and numerous libraries have been updated based on those scans.
Install in 2 easy steps
It's now easier than ever to try Entando. Get your own sandboxed instance on your local machine.